Somatic Genome Mosaicism Is Best Described as
Somatic mutations are a normal part of aging and occur throughout an organisms life cycle either spontaneously as a result of errors in DNA repair mechanisms or a direct response to stress. Simply defined mosaicism refers to the presence of two or more cell lines of different genetic or chromosomal material within one individual.

Solved 36 Somatic Genome Mosaicism Is Best Described As A Chegg Com
Somatic mosaicism is the accumulation of mutations in DNA sequence or copy number in cellular genomes after fertilization.
. In contrast to inherited mutations. Pathogenic mechanisms of somatic genome mosaicism. 6 using a combined pna and pcr assay.
Conclusion This is the first description of somatic NLRP3mosaicism detected using whole-exome sequencing in a mutation-negative patient with CINCA syndrome. 3 These were first described in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy but have since been described in. Pnas have been previously used as an effective pcr clamp to detect somatic mosaicisms of gnas mutations in blood dna of patients with mccunealbright syndrome.
Somatic mosaicism occurs when a postzygotic genetic variant is present in only a proportion of cells in the body. Although implicated in aging as early as the 1950s somatic mutations in normal tissue have been difficult to. 3 performed targeted-exome sequencing of 74 cancer genes in multiple biopsies from sun-exposed eyelid.
This process results in an organism composed of countless cells each with its own unique personal genome. The engine behind this is somatic mutagenesis. Genetic variation that is present in the genomes of cells that make up the body of the organism and do not contribute to gametes produced by the individual.
Whether mosaicism is clinically relevant is dependent on the tissue involved and the percentage of abnormal genetic material present in. When such mutations disrupt. De novo mutations occur and accumulate at all stages during the lifespan of an organism.
The fidelity capability of scDNA-seq allows detection of somatic mutations regardless of mosaicism level and has provided some of the first direct genome-wide measurements of somatic mutations. 2Center for Molecular Medicine and Genomics Wayne State University School of Medicine Detroit MI United States. 3 Martincorena et al.
Mosaic mutations can go unnoticed underlie genetic disease or normal human variation and may be transmitted to the next generation as constitutional variants. A Mutations that occur early in development are likely to expand clonally resulting in substantial proportions of cells in a tissue carrying the same mutation even in the absence of selection. Somatic mutations are present in both normal cells and in various diseases.
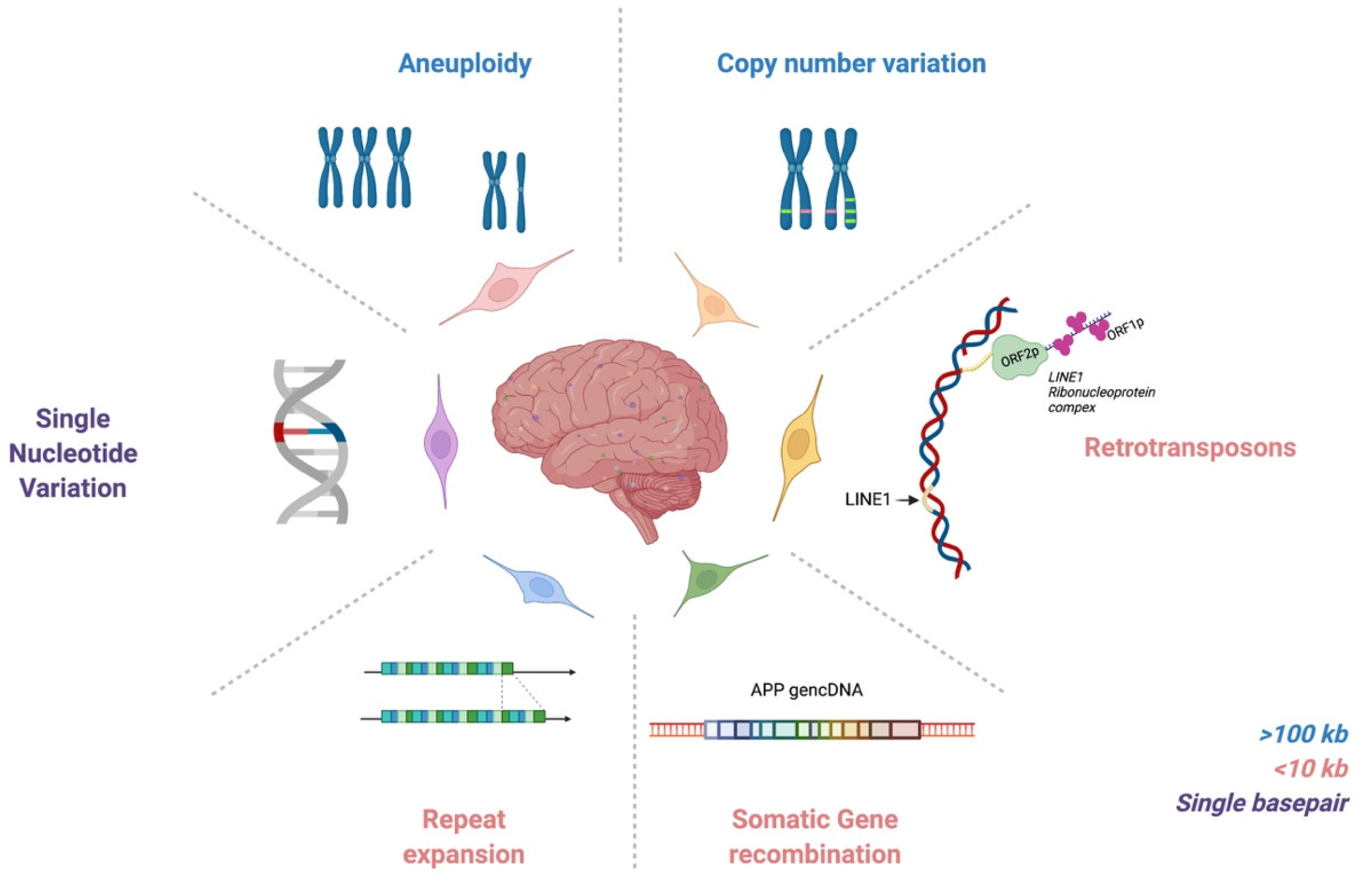
Age-related accumulation of postzygotic DNA mutations results in tissue genetic heterogeneity known as somatic mosaicism. In contrast to inherited mutations somatic mosaic mutations may affect only a portion of the body and are not transmitted to progeny. These mutations affect varying genomic sizes ranging.
In contrast to inherited mutations somatic mosaic mutations may affect only a portion of the body and are not transmitted to progeny. 1 2 Mosaic variants have been shown to cause familial diseases most commonly in disorders caused by genes with high mutational frequencies. Genetic mosaicism is defined as the presence of two or more cell lineages with different genotypes arising from a single zygote in a single individual.
Genetic variation that is present in the genomes of cells that specifically contribute to the gametes. Somatic variations have been suggested to play a major role in driving neuronal diversity and genome evolution. Somatic mosaicism refers to the occurrence of two genetically distinct populations of cells within an individual derived from a postzygotic mutation.
The somatic mosaicism observed in blood is strongly biased towards expansions and contributes not only to the progressive nature of the different symptoms in several DM1 ethnic groups but also to the variation in the age of onset 68910. Genetic mosaicism is a postzygotic mutation. 3Department of Pathology Wayne State University School of Medicine Detroit MI United States.
Thus every human is undoubtedly mosaic. The concept of genome mosaicism stems from the early 20thcentury when Boveri 1914 Morgan and Bridges 1919andothersspeculatedthatcancerwasasomaticmosaic causedbygeneticalterationsMutationswerethengenerallyun- derstoodtobesourcesofgeneticvariationthatalterthephysical andfunctional unitsofheredity. 1The Division of HematologyOncology Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan Ann Arbor MI United States.
Somatic genome mosaicism is best described as ALL OF THESE differences in genome sequence between cells of an organism due to errors incurred during division differences in gene location in the genome differences in proteins expressed between cells of an organism differences in genome sequence between cells of an organism due to tissue-specific expression. In tissues with proliferative cells such as skin and oesophagus genomic mosaicism can give rise to multiple competing clonal events that have been described as a patchwork of thousands of evolving clones. Mutations occurring early in development can cause mosaicism within the gene line impacting organism development.
This had initially been regarded as background noise but in retrospect is completely consistent with somatic mosaicism for the pF556L NLRP3mutation in this child with CINCA syndrome. The concept that all somatic cells have identical genomes needs to be replaced by a much more dynamic model of an increasingly mosaic genome. In contrast if distinct cell lines derived from different zygotes the term is now known as chimerism.
Somatic mutations are low-frequency events and only directly detectable when they are amplified in a clonal lineage Figure 2. Somatic mosaicism refers to the occurrence of two genetically distinct populations of cells within an individual derived from a postzygotic mutation. Somatic mosaicism refers to the occurrence of two genetically distinct populations of cells within an individual derived from a postzygotic mutation.

Solved Somatic Genome Mosaicism Is Best Described As All Of Chegg Com

Somatic Mutations In The Nervous System The Genome Is A Set Of Download Scientific Diagram

Genes Free Full Text Genomic Mosaicism Formed By Somatic Variation In The Aging And Diseased Brain Html
No comments for "Somatic Genome Mosaicism Is Best Described as"
Post a Comment